- HOME
- Know Your Tech
- Logistics management: A step-by-step implementation guide
Logistics management: A step-by-step implementation guide
- Last Updated : January 4, 2026
- 591 Views
- 14 Min Read
Have you ever noticed how some businesses fulfill orders within hours, while others take days for the same process? The difference comes down to how well their systems handle the flow of information and products from warehouse to customer.
Highlights
- Logistics management coordinates order processing, inventory, warehousing, transportation, and returns from supplier to customer.
- Modern logistics systems integrate order management, inventory tracking, shipment coordination, real-time visibility, returns processing, and performance analytics.
- Effective logistics management reduces fulfillment time, improves delivery accuracy, and lowers operational costs through automation.
- Implementation starts with assessing current workflows, defining specific goals, choosing the right platform, and automating high-impact processes.
- Building custom logistics apps lets businesses design systems that match their exact workflows, rather than forcing processes into generic software.
Logistics management creates the infrastructure to move orders smoothly through every stage, from initial placement through final delivery. Businesses with strong logistics systems can handle more orders with the same team, while also maintaining speed and accuracy as volumes increase.
This guide breaks down logistics management in detail, including its key functions and components. Find out how to implement logistics improvements step by step with examples.
What is logistics management?
Logistics management is the process of planning, executing, and monitoring the movement of goods from suppliers to customers via warehouses.
For instance, when a customer orders electronics online, logistics management ensures that the order is verified, inventory is checked at the nearest warehouse, the item is picked and packed correctly, shipping is coordinated with the best carrier, and the customer receives tracking updates. All of this happens automatically in the background.
Businesses that handle logistics well can fulfill orders faster, keep customers informed, and scale operations without increasing manual work or errors.
Top 5 functions of logistics management
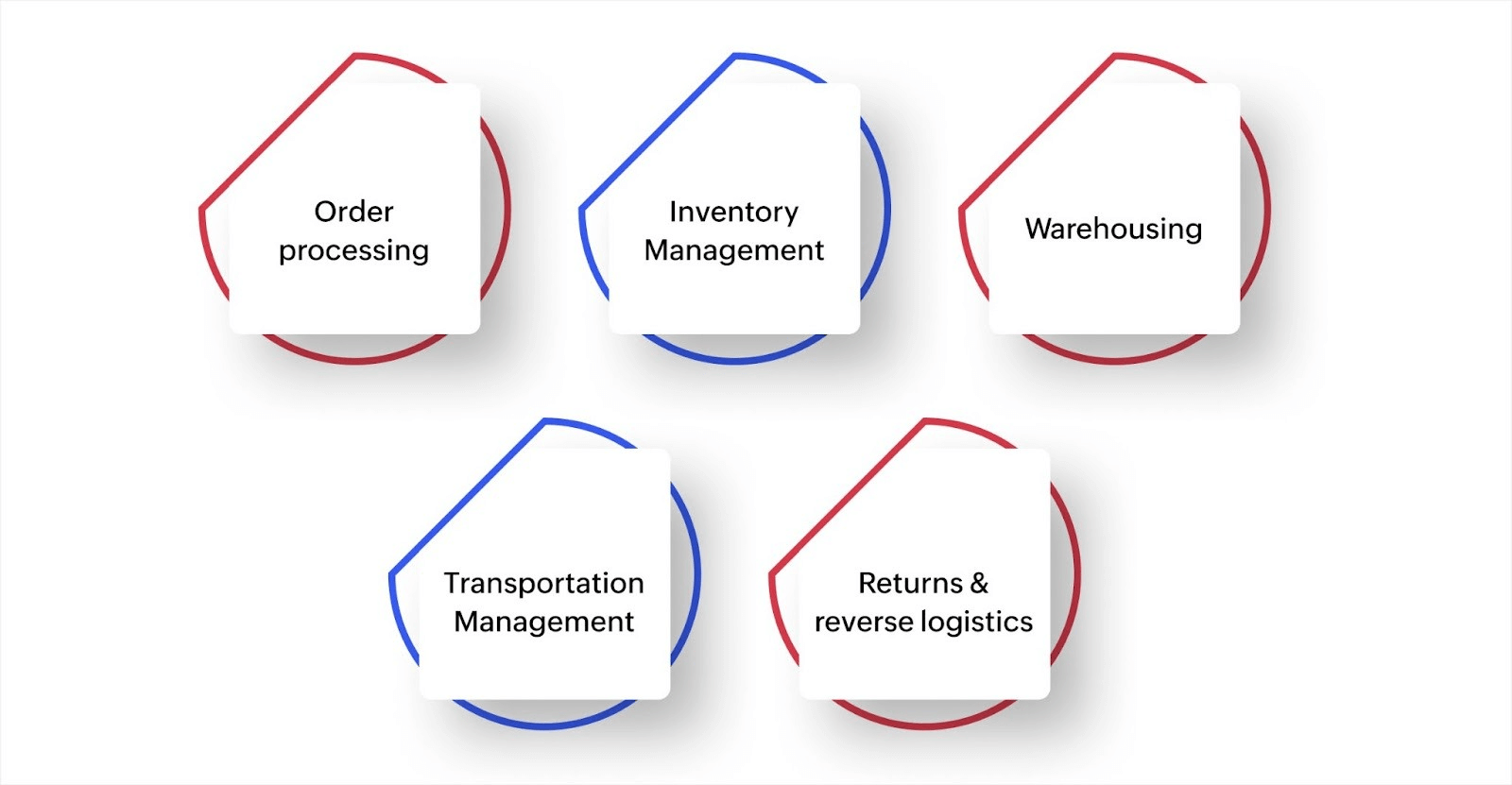
Logistics management combines several activities to move products efficiently. Each function handles a specific part of the fulfillment process, and when they're connected properly, orders flow smoothly from placement to delivery. Let’s take a look at those main functions now.
1. Order processing
This captures customer orders and verifies payment and product availability, then routes fulfillment instructions to the right location. Speed matters here because automated order processing eliminates manual data entry and starts fulfillment immediately after purchase.
For example, an e-commerce store selling home goods would receive orders through its website, mobile app, and marketplace listings. An integrated order-processing system can capture all of these orders in one place and automatically notify the warehouse team which items to pick and pack.
2. Inventory management
This tracks stock levels in real time across all storage locations, prevents selling products you don't have, and signals when reordering is needed. Accurate inventory data stops overselling situations and helps maintain optimal stock levels without tying up excessive cash in storage.
For instance, a furniture retailer operating physical showrooms and an online store could keep its inventory system synced across both channels. When a dining table sells in the store, the online catalog updates immediately so website visitors can see the current availability.
3. Warehousing
This covers how products are stored, organized, and retrieved for fulfillment. Smart warehousing uses location mapping, barcode scanning, and picking optimization to reduce the time between receiving an order and getting it ready for shipment.
Let's say a company fulfilling subscription boxes uses a warehouse management app that assigns specific shelf locations to each product. When orders come in, the system can generate optimized picking routes so warehouse staff can gather all of the needed items in the shortest path through the facility.
4. Transportation management
This handles carrier selection, route planning, shipment tracking, and delivery coordination. Good transportation management compares shipping options, chooses the most reliable and cost-effective carrier for each delivery, and provides visibility into where shipments are at any moment.
For example, a distributor shipping industrial supplies might use a dashboard showing all in-transit deliveries. When weather delays affect one region, the team can proactively contact affected customers and adjust delivery expectations before complaints arise.
5. Returns and reverse logistics
This manages product returns, inspections, restocking decisions, and refund processing. A smooth returns process actually increases customer confidence because knowing they can return items easily makes people more willing to buy.
For instance, an electronics retailer could build a returns app that lets customers request returns online, receive a prepaid shipping label, and receive automatic status updates as the returned item is received, inspected, and processed. This approach can significantly reduce return handling time.
Key components of a modern logistics management system
Modern logistics management requires more than basic tracking spreadsheets. Complete systems integrate multiple components that handle different parts of the fulfillment process while sharing data across the entire operation.
Here's what a complete system includes.
- Order management: Captures orders from all sales channels, validates information, checks inventory availability, and routes fulfillment instructions to the correct location automatically.
- Inventory and warehouse management: Tracks stock levels in real time across multiple locations, manages warehouse layouts and bin assignments, generates picking lists, and sends reorder alerts when stock runs low.
- Shipment and fleet management: Coordinates deliveries by assigning orders to drivers or carriers, optimizes delivery routes, tracks vehicle locations, and manages maintenance schedules for company-owned fleets.
- Real-time tracking: Provides visibility into order status from placement through delivery, shows current shipment locations, estimates delivery times, and sends automatic updates to customers.
- Returns processing: Handles return authorizations, tracks returned items through inspection and restocking, processes refunds or exchanges, and updates inventory when items return to available stock.
- Reporting and analytics: Monitors key metrics like delivery times, order accuracy rates, inventory turnover, and fulfillment costs to identify bottlenecks and track improvements over time.
These components work together as a single, connected system rather than as separate tools. When a customer places an order, the order management module checks inventory, the warehouse system generates picking instructions, shipment management coordinates delivery, tracking provides visibility, and analytics capture performance data—all automatically.
How to implement logistics management in your business, step by step
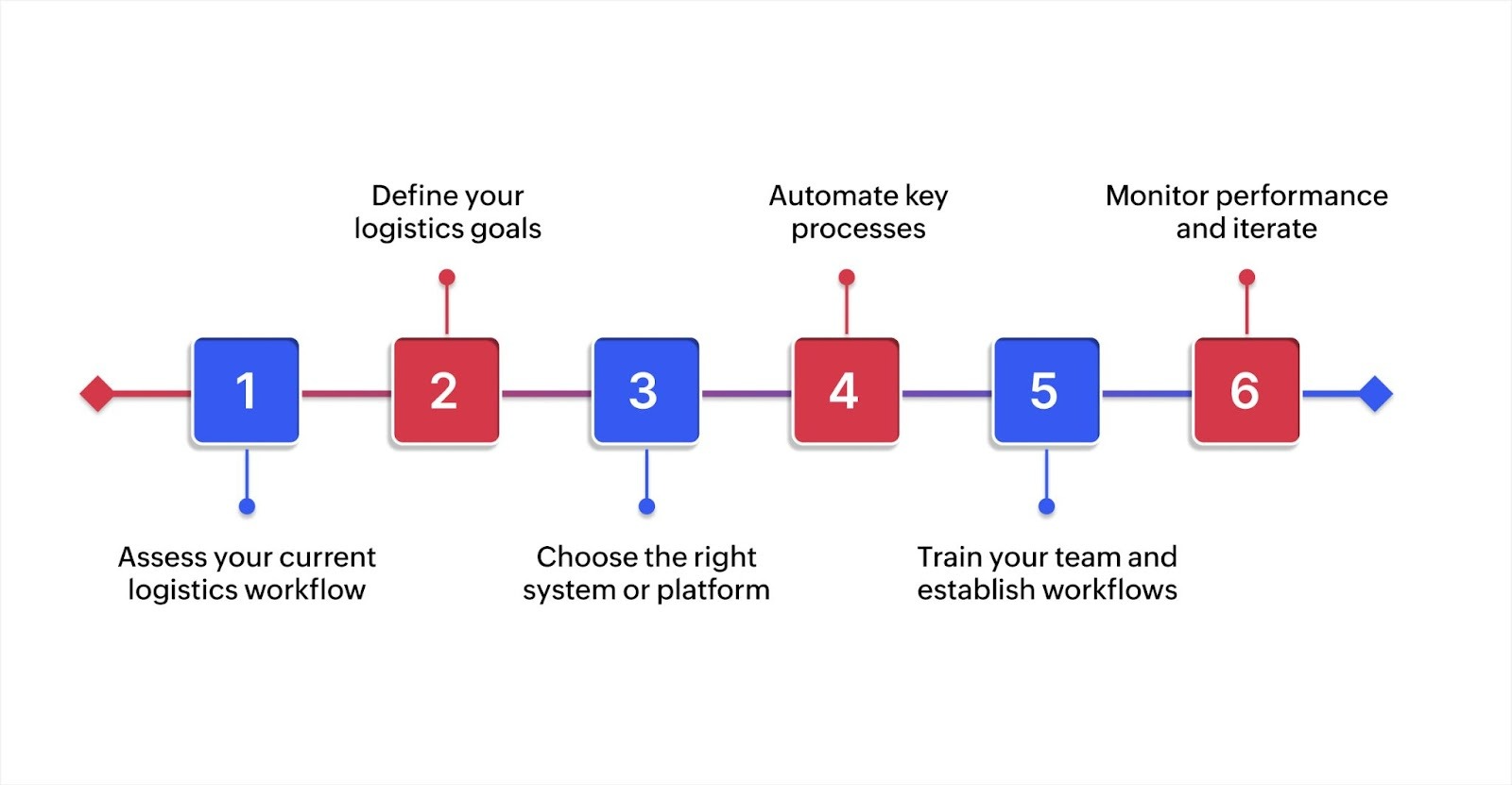
Implementing better logistics management doesn't mean replacing everything overnight. Most businesses improve logistics gradually by addressing the biggest challenges first, then expanding automation and integration over time.
Here's how to approach implementation.
Step 1: Assess your current logistics workflow
Map out how orders currently move through your system from placement to delivery. Document each step, identify where delays happen, and gather feedback from teams handling fulfillment. Look for common issues like:
- Manual handoffs: Systems or departments that pass information manually slow down order processing and create opportunities for errors.
- Disconnected tools: Multiple platforms that require duplicate data entry waste time and increase the risk of inconsistencies.
- Recurring errors: Specific stages where mistakes happen repeatedly create rework, delays, and customer dissatisfaction.
- Time-consuming coordination: Manual tasks that consume hours each day prevent teams from focusing on strategic improvements.
- Visibility gaps: Unclear order statuses frustrate both internal teams trying to answer questions and customers waiting for updates.
Tip: Walk through the complete order journey yourself. Place a test order and track exactly what happens at each stage, noting how long each step takes and where information gets lost or delayed.
Step 2: Define your logistics goals
Set specific targets for what you want to improve. Measurable goals give you clear direction and help evaluate whether changes are working. Focus on metrics like:
- Average order fulfillment time: Track how long it takes from placement to shipment to identify where delays occur.
- Order-processing error rate: Measure mistakes that cause returns or customer complaints to prioritize accuracy improvements.
- On-time delivery percentage: Monitor how often you meet customer expectations to gauge reliability.
- Customer inquiry volume: Count questions about order status to identify where visibility improvements are needed.
- Manual hours spent: Calculate the amount of time teams spend on coordination tasks to find the best automation opportunities.
Tip: Prioritize two or three high-impact goals rather than trying to improve everything at once. Choose improvements that directly affect customer experience or create the biggest operational bottlenecks.
Step 3: Choose the right system or platform
Evaluate solutions based on your business size, order volume, complexity, and growth plans. Consider key factors such as:
- Integration capability: Look for systems that connect with your existing e-commerce, accounting, and communication tools. Seamless integration means that orders flow automatically from sales channels to fulfillment without manual data transfers.
- Customization options: Determine whether you can adapt workflows to match your process or if you must change how your team works. Flexible platforms let you design around your business logic rather than forcing you into predefined templates.
- Scalability: Verify that the system handles two to five times your current volume without performance issues or expensive upgrades. The right solution grows with your business without forcing platform switches or dramatic fee increases.
- User experience: Assess whether your team can learn the system quickly without extensive training. Intuitive interfaces reduce onboarding time and increase adoption, while complex systems often lead to workarounds that undermine efficiency.
- Total cost: Calculate licensing, implementation, and maintenance costs compared to value delivered. Consider upfront expenses and recurring fees, including customization, support, and future upgrades.
Note: Pre-built software works well for standard workflows, but businesses with unique processes often benefit from customizable platforms that let them design systems that match their exact requirements.
Step 4: Automate key processes
Start by automating the most time-consuming or error-prone activities. Quick wins build momentum and demonstrate value to your team. Focus on these high-impact automation opportunities:
- Order routing: Automatically assign orders to the right warehouse or fulfillment location based on inventory and customer location.
- Inventory updates: Sync stock levels instantly when sales occur across all channels to prevent overselling.
- Customer notifications: Send order confirmations, shipping updates, and delivery alerts without manual intervention.
- Reorder alerts: Trigger notifications when inventory reaches specified thresholds so you never run out of popular items.
- Picking lists: Generate optimized warehouse picking instructions automatically to reduce fulfillment time.
Focus on automating one workflow completely before moving to the next. Partial automation often creates new coordination problems.
Step 5: Train your team and establish workflows
Make sure everyone using the new system understands how it works and what their responsibilities are. Use this training approach for implementation.
- Hands-on sessions: Run practical training for each team or role using real scenarios they'll encounter in daily operations.
- Quick reference guides: Create simple documentation for common tasks that staff can access when they need help.
- Power users: Designate experienced team members who can help others troubleshoot questions as they arise.
- Follow-up sessions: Schedule check-ins after initial use to address questions and gather feedback on what's working.
- Updated procedures: Document workflow changes and update standard operating procedures for consistency and new hire onboarding.
Tip: Involve team members in system design and testing. People who help build workflows are more likely to adopt them successfully because they’re invested in them.
Step 6: Monitor performance and iterate
Track the metrics that matter most to your goals. Review performance data regularly and make adjustments when you spot problems or opportunities.
Create a regular review schedule to catch issues early and track progress like this.
| Frequency | What to monitor |
| Daily | Immediate issues requiring quick fixes, like delayed shipments or system errors. |
| Weekly | Key metrics and emerging patterns in fulfillment performance. |
| Monthly | Progress toward goals and adjust strategies based on what's working. |
| Quarterly | Whether systems still meet business needs as you grow and markets change. |
Gather ongoing feedback from teams using the system. They often spot improvement opportunities that don't show up in reports.
Logistics management in action: Real-world workflow examples
Seeing how other businesses have solved specific logistics challenges provides practical insights you can adapt to your situation. These examples show the problems companies faced, the systems they built, and the measurable improvements they achieved.
Multi-channel e-commerce seller
America Ship, a logistics company on the Texas-Mexico border, built a complete custom logistics application to handle their cross-border shipping operations. They previously managed everything through spreadsheets and email chains, which couldn't handle growing data volumes and made collaborative work challenging.
They built a comprehensive system with nine integrated modules covering dashboard analytics, outbound shipments, inbound packages, customer management, shipment requests, website signup integration, help ticket management, cost calculation, and payment tracking. The dashboard provides real-time visibility into packages in inventory, pending payments, and shipments made.
Their cost calculator module integrates directly with their website, providing instant quotes to customers and eliminating the need for customer care executives to handle manual estimate requests. The system avoided costs of over $3,000 per month for programmers.
Multi-warehouse distributor
Air Rail, an aviation ground support equipment provider in Spain, scaled from managing 180 machines in three airports to 1,600 machines in more than 30 airports in seven countries. They grew their rental fleet while only expanding from two after-sales managers to six, achieving effective and efficient scaling.
They built a ground support equipment report application that serves as a single point of entry for all maintenance and service requests across their European network. The system also includes a sales assistant application tracking machine quotes, client relationships, and sales executive assignments throughout the equipment lifecycle.
Before implementing their custom logistics system, day-to-day operations relied on emails and spreadsheets, which became increasingly slow and inefficient as they expanded. Their previous self-service website also caused customer satisfaction issues due to instability.
DTC brand with high return volume
Lalamove, operating across 11 markets with 14 million customers and more than two million driver-partners, built a safety incident management platform to handle their high volume of incidents and returns across their on-demand logistics network.
Their system features an internal incident reporting form with dynamic fields that change based on priority level, case chronology recording, and multi-team collaboration capabilities spanning customer service, safety, sales, marketing, and driver operations teams.
Before building this custom platform, they used a standard customer service application that only captured one-sided incident documentation. They couldn't communicate effectively with other teams, missed details of follow-up actions, and struggled to provide local authorities with easy case information retrieval.
The platform now gathers all incident information in a single place that’s accessible to everyone who needs it. Handling safety incidents requires more than a customer service application because many teams are involved in resolving each incident.
B2B supplier with complex ordering
Duratuf Products, a New Zealand rubber and PVC manufacturer serving 3,000+ customers across 47 countries, built a comprehensive three-module logistics management application to handle their complex contract manufacturing and transportation coordination.
Their pre-dispatch module handles distance calculation, delivery cost estimation, material inspection tracking, sales order confirmation, and transportation cost finalization.
The dispatch module manages transport document attachment, payment terms tracking, pricing basis recording, and weightage assignment. The delivery module tracks delivery status, evaluates performance, monitors delayed or expedited deliveries, and confirms order completion.
They manage 30 users across different levels, including warehouse executors, store executors, and operational managers. The system also automates document creation, converts sales orders to invoices, maintains PIN code lists, includes a built-in cost calculator, and creates pallet labels, achieving a 10x reduction in time spent on task management.
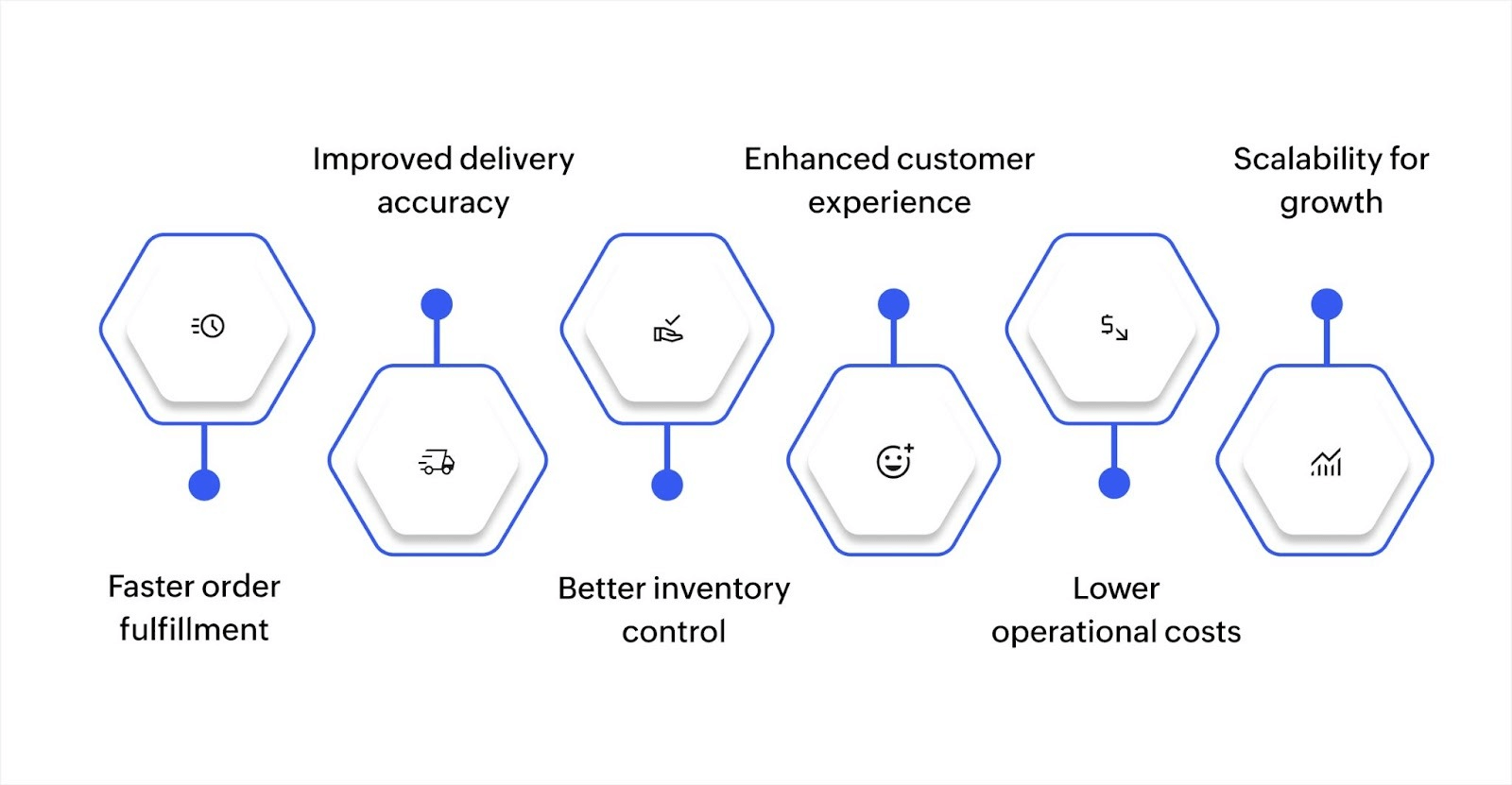
6 benefits of effective logistics management
Recent data shows that U.S. business logistics costs reached $2.3 trillion, accounting for 8.7% of the country’s GDP. This demonstrates how essential logistics management is to business operations across every industry. Let’s look at some of the top benefits of logistics management now.
1. Faster order fulfillment
Automation and connected systems eliminate delays between order stages. Orders can move from placement to shipment in hours instead of days because manual coordination disappears and handoffs happen automatically.
2. Improved delivery accuracy
Automated data validation and real-time inventory tracking reduces errors that cause incorrect items, quantities, or shipments to the wrong addresses. Barcode scanning and automated picking lists help warehouse teams avoid mistakes that lead to returns and customer complaints.
3. Better inventory control
Real-time visibility into stock levels across locations prevents overselling and helps maintain optimal inventory without excessive safety stock. Automated reorder alerts ensure that popular items stay available while slow-moving products don't tie up warehouse space and cash.
4. Enhanced customer experience
Meeting delivery expectations and providing tracking visibility builds trust and increases repeat purchases. Customers appreciate knowing exactly when orders will arrive and receiving proactive updates about any delays.
5. Lower operational costs
Automation reduces manual labor requirements for order processing, inventory updates, and coordination tasks. Better routing and carrier selection cut shipping costs, while improved inventory management reduces carrying costs and waste from obsolete stock.
6. Scalability for growth
Connected logistics systems handle increased order volumes without proportionally increasing manual work or coordination overhead. Businesses can grow significantly using the same core team because automation handles the volume increase.
Common challenges in logistics management and how to address them
Logistics improvements require careful planning to handle common obstacles. Recognizing these challenges early helps you plan around them and avoid common mistakes.
Disconnected systems
When order data lives in one place, inventory in another, and shipping in a third system, teams waste time manually syncing information, and errors multiply at each handoff.
Solution: Use integration platforms or unified logistics systems where all data flows automatically between components, eliminating the need for manual transfers.
Limited visibility
Without real-time tracking, teams can't answer customer questions about order status, identify delayed shipments proactively, or spot patterns in fulfillment problems.
Solution: Implement tracking systems that update order status automatically and provide dashboards showing the current state across all orders and shipments. This gives your team the visibility they need to respond quickly.
Manual bottlenecks
Repetitive tasks like data entry, sending notifications, updating spreadsheets, and coordinating between departments slow fulfillment and create opportunities for human error.
Solution: Automate routine workflows, starting with the most time-consuming or error-prone processes. This way, you can free up your team to focus on strategic work that requires human judgment.
Scaling difficulties
Systems that work for modest order volumes often break down as volume increases, forcing businesses to add more people or tools just to maintain current service levels.
Solution: Choose platforms designed to handle growth, where increased volume doesn't require proportional increases in manual work or system complexity.
Customer communication gaps
When customers don't know their order status, expected delivery dates, or how to handle problems, they contact support repeatedly, creating unnecessary overhead.
Solution: Set up automated notifications that keep customers informed at key stages like order confirmation, shipment notification, delivery updates, and resolution of any issues, reducing support inquiries significantly.
Build custom logistics management systems with Zoho Creator
Generic logistics software often forces businesses to adapt their workflows to rigid templates, creating new inefficiencies when unique processes don't fit standard features. Customization options in traditional platforms are limited and expensive, leaving businesses choosing between compromising their workflow or paying for extensive development.
Zoho Creator is an AI-powered low-code application development platform that helps you build logistics management systems tailored to your exact workflow. You can design custom order processing, inventory tracking, shipping coordination, and delivery management without extensive coding.
What makes Zoho Creator unique is the visual builders and AI assistance that help you create apps matching your business logic rather than forcing you to change how you work. You can build automated workflows that activate actions based on status changes, create real-time dashboards for visibility across operations, and connect with your existing tools through 1,000+ integrations.
Businesses that build logistics systems matching their exact needs gain competitive advantages through speed and reliability. Start your 15-day free trial and see how quickly you can create apps that help you fulfill orders faster while maintaining the flexibility to adapt as your business grows.
FAQ
1. How does logistics management differ from supply chain management?
Supply chain management covers the entire product lifecycle from sourcing raw materials through manufacturing to customer delivery. Logistics management is one part of this, focusing specifically on moving and storing goods within that broader system.
2. What software do companies use for logistics management?
Companies use various solutions, including warehouse management systems, transportation management platforms, inventory tracking tools, and integrated logistics platforms. Many businesses build custom systems matching their specific workflows using low-code development platforms.
3. How do you calculate logistics costs?
Calculate logistics costs by adding transportation expenses, warehouse storage fees, labor costs, packaging materials, technology systems, and insurance. Track these as a percentage of revenue to benchmark efficiency and identify areas where you can reduce spending.
4. What metrics should you track in logistics management?
Key metrics include order fulfillment time, delivery accuracy rate, on-time delivery percentage, inventory turnover, carrying costs, return rate, and customer satisfaction scores. Track metrics aligned with your specific improvement goals to measure progress effectively.
5. How does automation improve logistics efficiency?
Automation eliminates manual data entry, reduces coordination time between departments, triggers actions based on status changes, updates inventory in real time, and handles routine communications. This speeds fulfillment while reducing errors and freeing teams for strategic work.
 Stephen
StephenStephen is a product marketer at Zoho Creator. An avid writer, he plies his trade evangelizing low-code during the day and pens songs at night. Sneakerhead and sushi enthusiast too.